Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 2; Pulse radiolysis measurement of local (partial) viscosity of pore water
retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 2; Pulse radiolysis measurement of local (partial) viscosity of pore waterNagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Ito, Tatsuya; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Tamaki, Ryoya*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen molecules (H ) retained by highly viscous suspension such as a carbonate slurry exist in the pore water of suspension in the form of gas (bubble). The H
) retained by highly viscous suspension such as a carbonate slurry exist in the pore water of suspension in the form of gas (bubble). The H behaviors such as the reaction of dissolved species of H
behaviors such as the reaction of dissolved species of H and the process forming H
and the process forming H bubble are mainly determined by the viscosity of pore water, while the H
bubble are mainly determined by the viscosity of pore water, while the H retention by the macroscopic viscosity of suspension. Such local (partial) viscosity is generally unclear. In order to clarify the H
retention by the macroscopic viscosity of suspension. Such local (partial) viscosity is generally unclear. In order to clarify the H retention/release mechanism in the suspension, it is important to estimate this viscosity. In this report as the second in a series of presentations, the reaction (decay) rate of hydrated electrons (e
retention/release mechanism in the suspension, it is important to estimate this viscosity. In this report as the second in a series of presentations, the reaction (decay) rate of hydrated electrons (e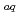
 ) formed as a radiolysis radical of pore water was transiently measured by using ns-pulse radiolysis, and the viscosity of pore water was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.
) formed as a radiolysis radical of pore water was transiently measured by using ns-pulse radiolysis, and the viscosity of pore water was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.